PCB Assembly Blog
-
Types of Electrical Test for PCB
Posted by
–
 Read more: Types of Electrical Test for PCB
Read more: Types of Electrical Test for PCBIntroduction to PCB Electrical Tests Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in modern electronic devices. To ensure the reliability and functionality of PCBs, various electrical tests are performed at different stages of the manufacturing process. These tests help identify defects, verify the board’s performance, and ensure compliance with industry […]
-
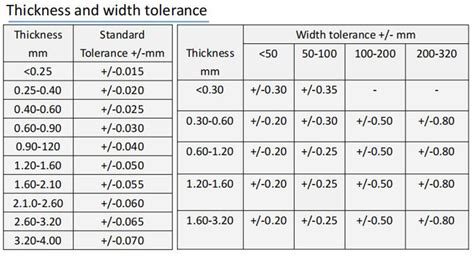
Tolerances on Copper Thickness on a PCB
Posted by
–
 Read more: Tolerances on Copper Thickness on a PCB
Read more: Tolerances on Copper Thickness on a PCBUnderstanding Copper Thickness and Its Importance in PCB Manufacturing Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronic devices, connecting and supporting various components to ensure proper functionality. One crucial aspect of PCB manufacturing is the copper thickness, which plays a vital role in determining the board’s electrical and […]
-
The Optimum PCB Design Flow – Right First Time
Posted by
–
 Read more: The Optimum PCB Design Flow – Right First Time
Read more: The Optimum PCB Design Flow – Right First TimeIntroduction to PCB Design Optimization Printed Circuit Board (PCB) design is a complex process that involves multiple stages and requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and manufacturability. Getting the PCB design right the first time is crucial to avoid costly redesigns, delays, and potential product […]
-
FR4 Quality – What to Expect
Posted by
–
 Read more: FR4 Quality – What to Expect
Read more: FR4 Quality – What to ExpectWhat is FR4? FR4 (Flame Retardant 4) is a composite material composed of woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin binder. The “FR” designation indicates that the material is flame retardant, while the “4” refers to the specific grade of the material. FR4 is known for its high strength-to-weight […]
-
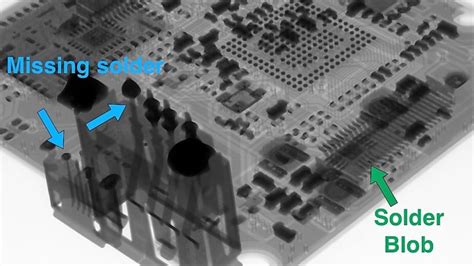
What is x-ray inspection in PCB?
Posted by
–
 Read more: What is x-ray inspection in PCB?
Read more: What is x-ray inspection in PCB?Why is PCB X-ray Inspection Important? PCB X-ray inspection is crucial for several reasons: Detecting hidden defects: X-ray inspection can reveal defects that are not visible to the naked eye or other inspection methods, such as optical inspection. Ensuring product quality: By identifying and addressing defects early in the manufacturing […]
-
Choose the Right Test Head
Posted by
–
 Read more: Choose the Right Test Head
Read more: Choose the Right Test HeadWhat is a TestHead? A test head, also known as a test fixture or test socket, is a specialized device used to establish a temporary electrical connection between the device under test (DUT) and the testing equipment. It serves as an interface that allows the testing equipment to send signals […]
-
PCB Solver – Outline/Milling Editor
Posted by
–
 Read more: PCB Solver – Outline/Milling Editor
Read more: PCB Solver – Outline/Milling EditorKey Features of PCB Solver Intuitive User Interface PCB Solver boasts an intuitive and easy-to-use interface that makes navigating the software a breeze. The well-organized layout and clearly labeled tools ensure that users can quickly access the features they need without any confusion. Extensive Library of Components One of the […]
-
What is an open on a PCB?
Posted by
–
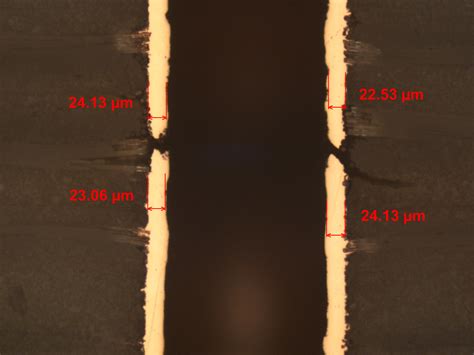 Read more: What is an open on a PCB?
Read more: What is an open on a PCB?Understanding PCB Opens An open, also known as an open circuit, is a common type of defect that can occur on a printed circuit board (PCB). In this article, we will dive deep into what PCB opens are, their causes, how to detect them, and methods for preventing and repairing […]
-
 Read more: Solder profiles and oven parameters for the eC-reflow-mate
Read more: Solder profiles and oven parameters for the eC-reflow-mateIntroduction to Solder profiles Solder profiles are essential for achieving optimal results in electronic assembly processes, particularly when using reflow ovens like the eC-reflow-mate. A solder profile is a temperature curve that defines the heating and cooling rates, as well as the time spent at specific temperatures during the reflow […]
-
What is the galvanic process of electrolysis?
Posted by
–
 Read more: What is the galvanic process of electrolysis?
Read more: What is the galvanic process of electrolysis?How Galvanic electrolysis Works In galvanic electrolysis, two dissimilar metals are immersed in an electrolyte solution and connected by an external circuit. The metal with the more negative reduction potential acts as the anode and undergoes oxidation, losing electrons. The metal with the more positive reduction potential acts as the […]




