Understanding PCB Opens
An open, also known as an open circuit, is a common type of defect that can occur on a printed circuit board (PCB). In this article, we will dive deep into what PCB opens are, their causes, how to detect them, and methods for preventing and repairing them.
What is a PCB Open?
A PCB open is a defect where there is an unwanted break or gap in a conductive pathway on a printed circuit board. This discontinuity prevents electrical current from flowing through the affected circuit, leading to a malfunctioning or non-functioning PCB.
Causes of PCB Opens
There are several reasons why opens can occur on a PCB:
-
Manufacturing Defects: Incomplete etching, incorrect drill sizes, or damage during the PCB fabrication process can result in opens.
-
Mechanical Stress: Excessive bending, twisting, or impact can cause traces or vias to crack or break, creating opens.
-
Thermal Stress: Exposure to extreme temperatures or rapid temperature changes can lead to opens due to the expansion and contraction of materials.
-
Chemical Contamination: Exposure to corrosive chemicals or improper cleaning can degrade the conductive pathways, resulting in opens.
-
Aging and Wear: Over time, the materials on a PCB can deteriorate, leading to cracks or breaks in the conductive pathways.
Detecting PCB Opens
Identifying opens on a PCB is crucial for troubleshooting and repair. Here are some common methods for detecting PCB opens:
Visual Inspection
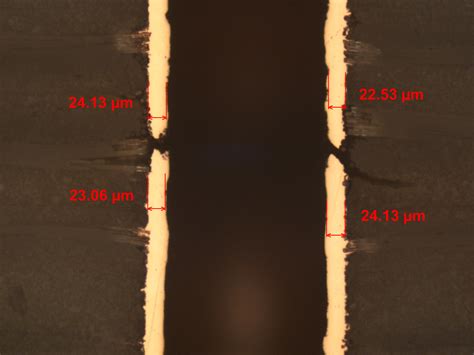
A visual examination of the PCB can sometimes reveal opens, especially if they are large or located on the surface. Using a magnifying glass or microscope can help identify hairline cracks or breaks in the traces or vias.
Continuity Testing
Continuity testing involves using a multimeter to check for electrical continuity between two points on a PCB. If there is no continuity where there should be, it indicates an open in the circuit.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI machines use high-resolution cameras and advanced image processing algorithms to detect opens and other defects on a PCB. This method is fast and efficient for inspecting large volumes of boards.
X-ray Inspection
X-ray inspection can reveal opens in the inner layers of a multi-layer PCB, which are not visible through visual inspection. This method is particularly useful for identifying opens in vias or buried traces.
Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging cameras can detect opens by identifying areas on the PCB that are not generating heat as expected due to a lack of electrical current flow.
Preventing PCB Opens
Preventing opens from occurring on a PCB is essential for ensuring reliable and long-lasting performance. Here are some strategies for preventing PCB opens:
Robust PCB Design
Proper PCB design is crucial for minimizing the risk of opens. This includes:
- Using appropriate trace widths and spacing
- Avoiding sharp angles or abrupt changes in trace direction
- Incorporating strain relief features for connectors and components
- Selecting materials with suitable thermal and mechanical properties
Quality Manufacturing Processes
Ensuring that the PCB manufacturing process adheres to strict quality control standards can help prevent opens. This includes:
- Proper etching and plating techniques
- Accurate drilling and hole sizing
- Careful handling and packaging of the PCBs
- Thorough cleaning and inspection procedures
Controlled Environment
Exposing PCBs to harsh environmental conditions can increase the risk of opens. Controlling the environment in which PCBs are stored, handled, and used can help prevent opens. This includes:
- Maintaining appropriate temperature and humidity levels
- Protecting PCBs from mechanical stress and impacts
- Avoiding exposure to corrosive chemicals or contaminants
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Regularly inspecting and maintaining PCBs can help identify and address potential open issues before they cause failures. This includes:
- Periodic visual inspections
- Cleaning and re-coating of PCBs as needed
- Monitoring environmental conditions
- Replacing aging or worn components

Repairing PCB Opens
When an open is detected on a PCB, there are several methods for repairing it, depending on the location and severity of the open. Here are some common repair techniques:
Jumper Wire Repair
For opens on the surface of the PCB, a jumper wire can be soldered across the break to restore electrical continuity. This method is quick and easy but may not be suitable for high-frequency or high-current applications.
Trace Repair
If the open is in a trace on the surface of the PCB, the damaged section can be scraped away, and a new trace can be applied using conductive ink or epoxy. This method requires steady hands and precision but can be effective for small repairs.
Via Repair
Opens in vias can be repaired by drilling out the damaged via and replacing it with a new one. This method requires specialized equipment and skills but can restore the electrical connection between layers of the PCB.
Rework and Replacement
In some cases, the best solution may be to remove the damaged component or section of the PCB and replace it with a new one. This method is more time-consuming and costly but can be necessary for severe damage or hard-to-repair opens.
Conclusion
PCB opens are a common defect that can cause significant issues in the functionality and reliability of electronic devices. Understanding the causes, detection methods, prevention strategies, and repair techniques for PCB opens is essential for anyone involved in PCB design, manufacturing, or maintenance.
By following best practices in PCB design, manufacturing, and handling, the risk of opens can be minimized, leading to higher-quality and more reliable PCBs. When opens do occur, prompt detection and appropriate repair methods can help restore the PCB to proper functioning and extend its lifespan.
FAQ
-
What is the difference between an open and a short on a PCB?
An open is a break or gap in a conductive pathway, preventing current from flowing through the circuit. A short, on the other hand, is an unintended connection between two or more conductive paths, allowing current to flow where it should not. -
Can PCB opens be detected by visual inspection alone?
While some opens, especially large ones or those on the surface, can be detected by visual inspection, others may require additional testing methods such as continuity testing, automated optical inspection, x-ray inspection, or thermal imaging. -
What is the most common cause of PCB opens?
The most common causes of PCB opens are manufacturing defects, mechanical stress, and thermal stress. However, opens can also result from chemical contamination, aging, and wear. -
How can I prevent opens in my PCB designs?
To prevent opens in your PCB designs, follow best practices such as using appropriate trace widths and spacing, avoiding sharp angles, incorporating strain relief features, selecting suitable materials, and specifying proper manufacturing processes and handling procedures. -
Is it always necessary to repair PCB opens?
The decision to repair PCB opens depends on the impact of the open on the functionality and reliability of the device. Some opens may not affect the performance of the PCB, while others may cause critical failures. A thorough assessment of the open and its potential consequences should be conducted before deciding on a repair strategy.
| Cause of PCB Open | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing Defects | Ensure proper etching, drilling, and quality control processes |
| Mechanical Stress | Incorporate strain relief features and handle PCBs with care |
| Thermal Stress | Select materials with appropriate thermal properties and control environmental conditions |
| Chemical Contamination | Avoid exposure to corrosive chemicals and ensure proper cleaning |
| Aging and Wear | Conduct regular inspections, maintenance, and replace worn components |





Leave a Reply